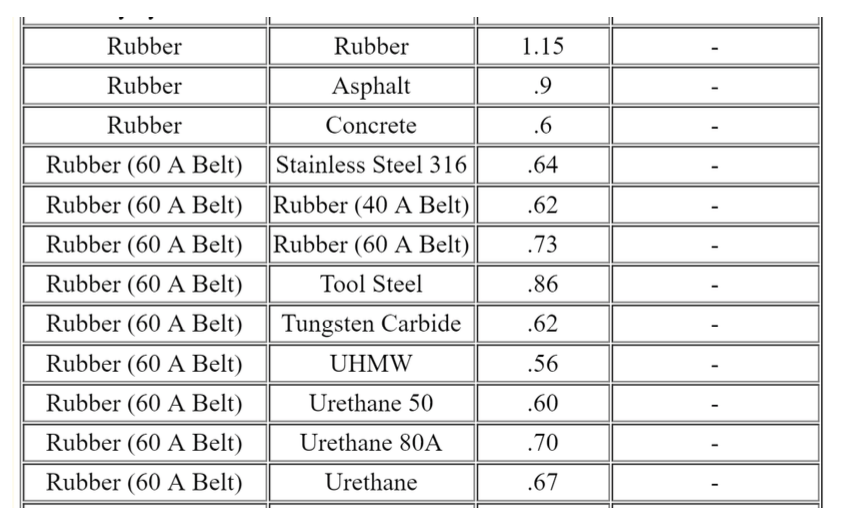
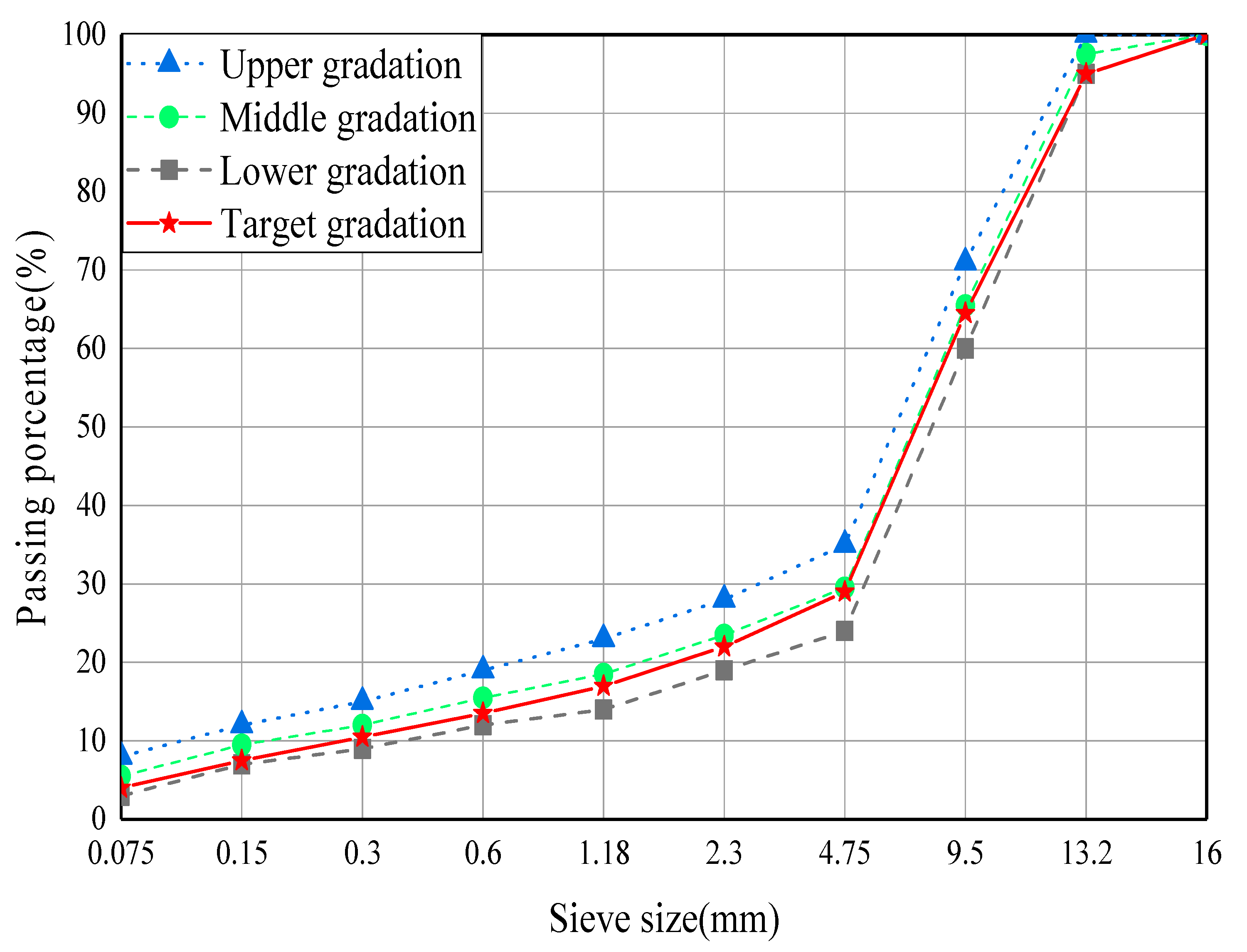
Rubber against rubber results in a static coefficient of friction of 1 15 whereas rubber against asphalt results in a static coefficient of friction of 0 9.
Coefficient of friction rubber on asphalt.
Viii rubber tires have a much higher coefficient of friction than iron tires especially on dry hard surfaces.
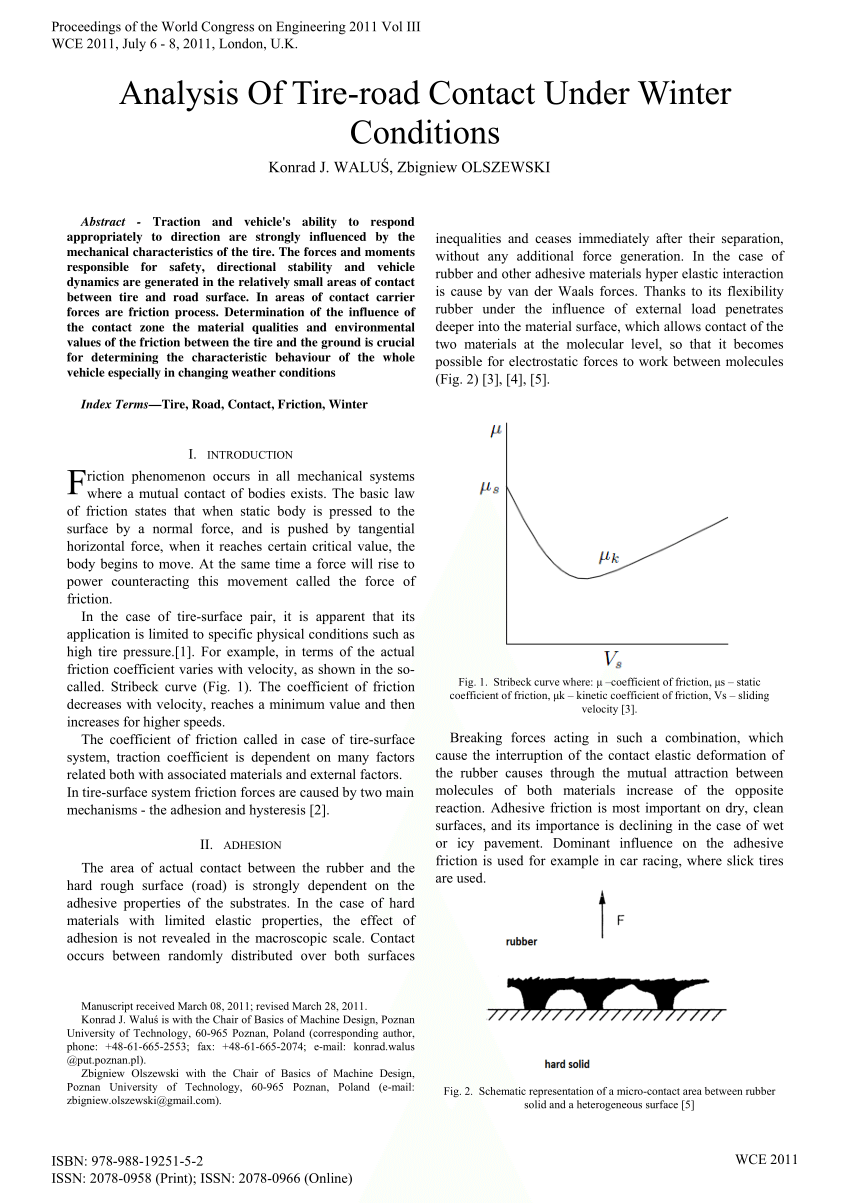
In this paper the thermodynamic model is based on equilibrium between frictional energy from hysteresis.
However the friction depends on csqd over a wide range of wave vectors q.
In general the hysteresis contribution to rubber friction increases with increasing magnitude of csqd.
For example static friction can prevent an object from sliding down a sloped surface.
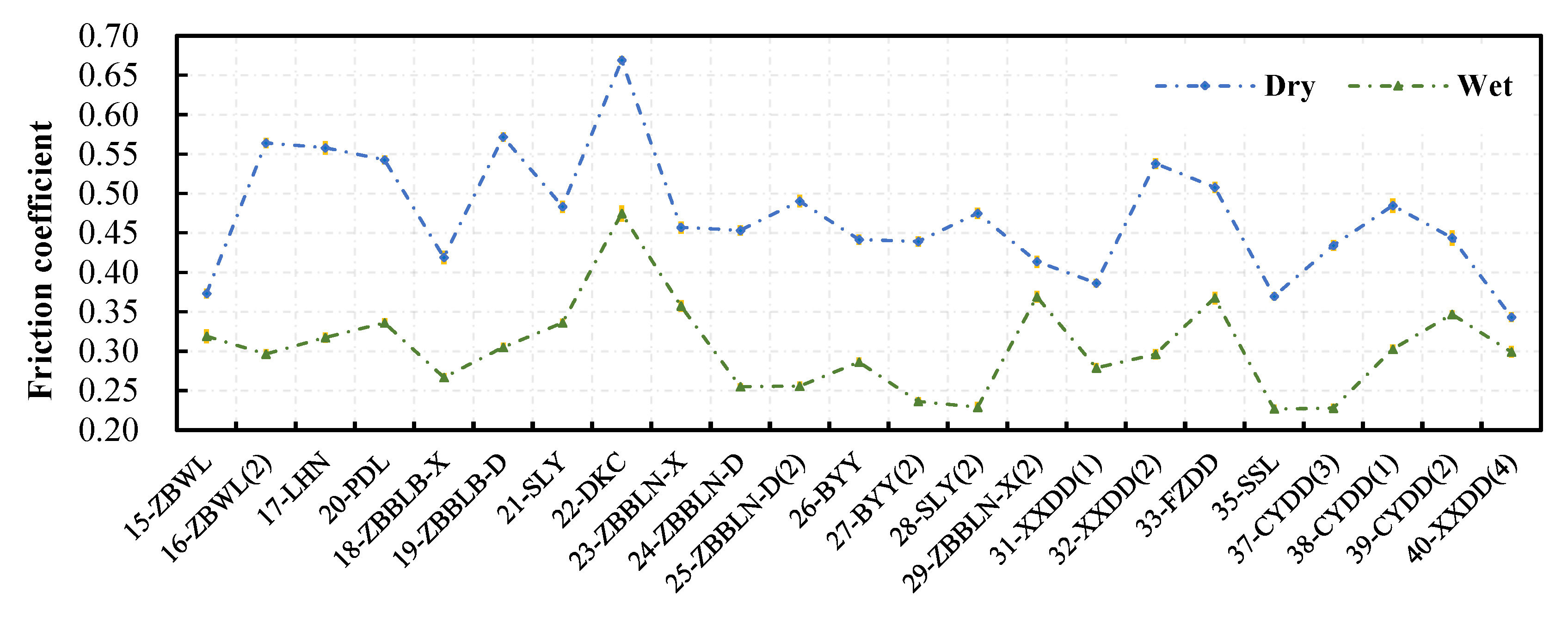
Rubber dry asphalt 0 9 0 5 0 8 1 rubber wet asphalt 0 25 0 751 rubber dry concrete 0 6 0 851 rubber wet concrete 0 45 0 751 silver silver 1 4 0 55 sapphire sapphire 0 2 0 2 silver silver 1 4 0 55 skin metals 0 8 1 0 steel steel 0 8 0 16 straw fiber cast iron 0 26 straw fiber aluminum 0 27 tarred fiber cast iron 0 15 tarred fiber aluminum 0 18 teflon teflon 0 04 0 04 0 041.
Ix the static friction is 10 to 20 per cent higher than the dynamic friction.
For example the rubber friction on asphalt road surfaces depends on csqd for q0 q q1 where typically q0.
Hence the friction is partially generated by viscosity of the water film.
Friction model of rubber and asphalt pavement under ice condition.
Treadwear friction coefficient for street tires on dry asphalt only 10 treadwear.
Vii the coefficient of friction depends on the type of road surface its de formability and especially on the presence or absence of dust mud or water.
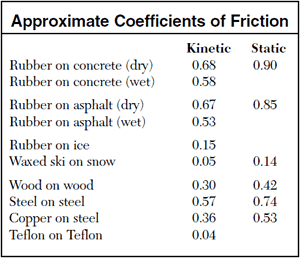
0 15 waxed ski on snow.
When rubber slides on a hard rough surface with rough ness on the length scales l it will be exposed.
At high enough velocity a thin continuous water film is generated between friction pair due to melting of ice resulting from frictional heating.
Less is known about the short distance cutoff l1 but i will argue later that in the context of rubber friction it may be taken to be of order a few mm so that the length scale region over which the road surface may be assumed to be fractal may extend over 3 orders of magnitude.
It is important to note that in addition to the coefficient of friction depending upon the materials that are in contact this coefficient is different for materials that are in motion.
Rubber on concrete dry 0 68.
Rubber on asphalt wet 0 53 rubber on ice.