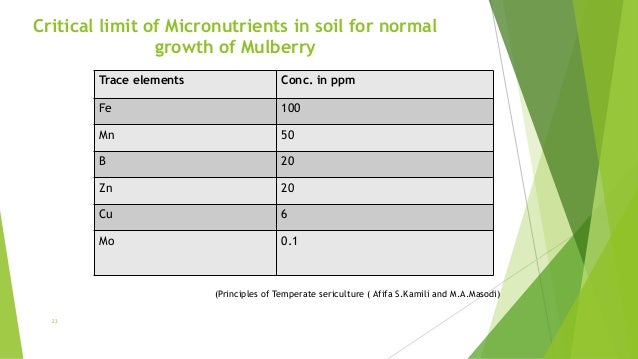
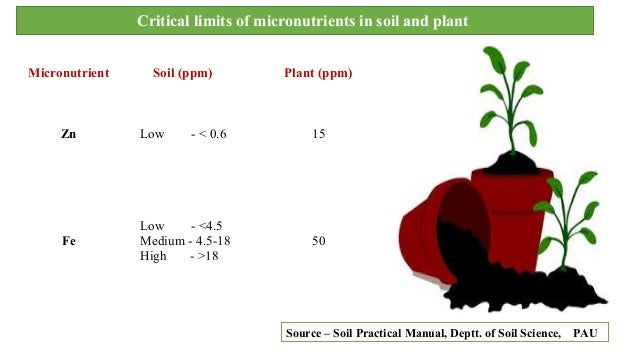
From the results of the present study an appropriate critical limit of deficiency range of 2 1 3 74 mg zn kg 1 for soil and 27 0 53 8 mg zn kg 1 for leaf can be fixed for getting maximum ginger yield in an ustic humitropept.
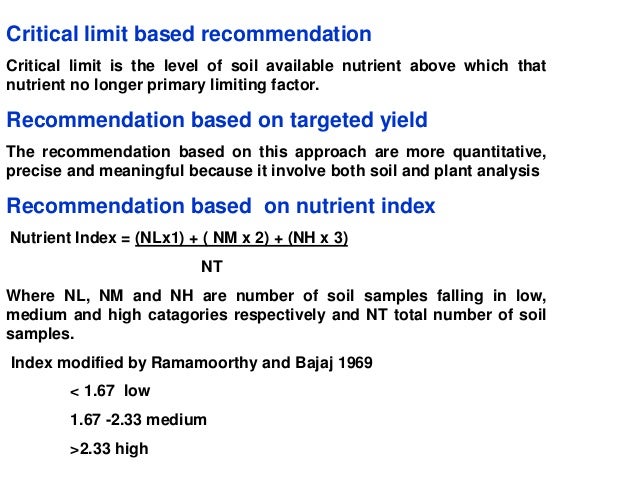
Critical limit of zinc in soil.
According to the graphical procedure of cate and nelson 1965 using a scatter diagram the critical limit of available zinc was 0 69 mg kg 1 whereas the critical concentration of zinc in 50 days old pea plant tissue was 0 21 per cent.
The critical limits of zinc in soils and plants are 2 68 mg kg 1 and 12 26 mg kg 1 respectively.
If the concentration of nickel in your soil is greater than 7400 mg kg it would be a good idea to test the food grown in your soil and seek expert advice about whether you need to take special corrective action in the levels are high.
Dry matter yield zinc content and zinc uptake by the plant also increases as the level of zinc increases.
Zinc is one of the essential plant micronutrients and its importance for crop productivity is similar to that of major nutrients.
In all the soils testing below 0 78 ppm zn plants responded to zn application and the per cent mean response at 5 and 10 ppm added zn levels was 101 21 and 111 38 respectively.
The soil available zn was positively correlated with ph r 0 68 oc r 0 243 available n r 0 236 available p r 0 364 and also positive and significant correlations with sand r 085 clay r 052.
The average response in dry matter yield at optimum level of.
Ideally for healthy and productive soil the concentration of zinc should be 1 200 mg kg.
The critical zn concentration in soil and plant below which plant response to zn application to the soil may be expected was 0 78 and 19 ppm respectively.
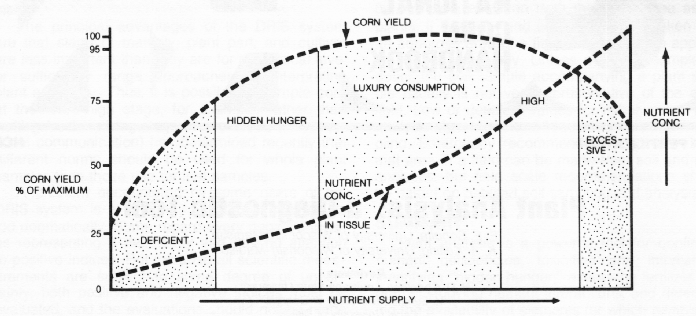
Zinc in common with the other micronutrients can affect growth when its content is either lower or above a critical level due to deficiency and or toxicity problems respectively.
The soil contained caco3 0 33 7 54 ph 6 2 8 8 ec 0 27 1 6 dsm 1 and organic carbon 2 7 11 4 g kg 1.
For the whole young plant values reported include 8 mg zn kg for sorghum and 25 mg zn kg in winter wheat and chickpea.
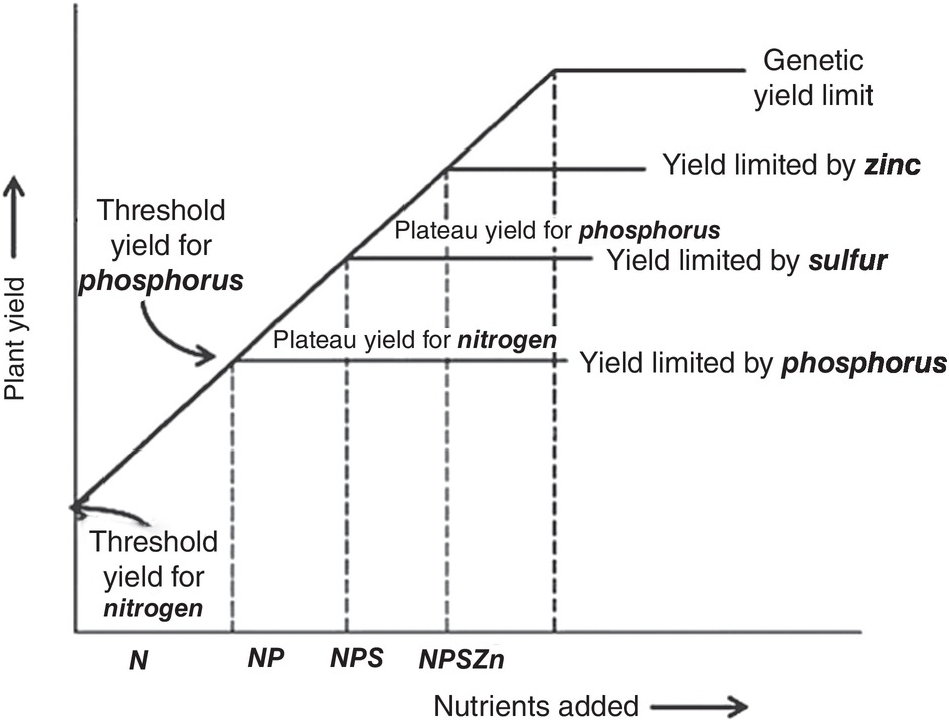
The use of various sufficiency levels of yield resulted in a wide range of critical limits.
According to the graphical procedure of cate and nelson 1965 using a scatter diagram the critical limit of available zinc was 0 69 mg kg 1 whereas the critical concentration of zinc in 50 days.